We live in the information age, and most of what we do is greatly influenced by our ability to access vast amounts of data. It can be via the Internet, our computers, or our mobile phones. The buzzword describing this amount of information is Big Data.
Before we get to the definition of big data, we must know what data is?
It is the raw form of information before the sorting, arranging, and processing operations. It cannot be used in its primary form before processing.
The raw data can be divided into three types:

- Structured: These are data organized in tables or databases.
- Unstructured: It constitutes the largest percentage of data, and it is the data that people generate daily from text writings, pictures, videos, messages, clicks on websites.
- Semi-structured: a type of structured data, but the data is not in the form of tables or databases.
Now, what is big data?

The term Big Data stands for multiple data types and sources with a huge size. It has huge importance, as it provides a highly competitive advantage for companies if they can benefit from it and process. Big Data provides a deeper understanding of the company customers’ behavior and their requirements. This helps to make appropriate decisions within the company in a more effective way. Thus, increasing efficiency and profit and reducing Losses.
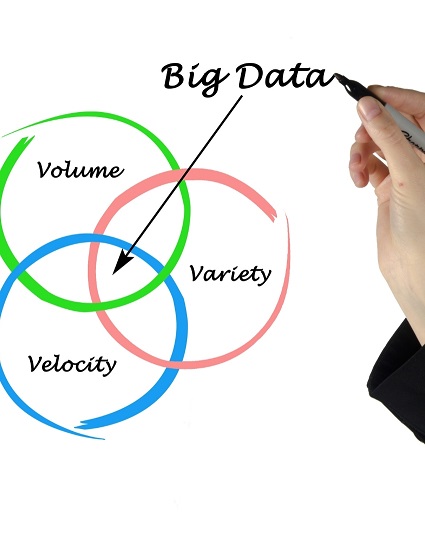
Characteristics
Volume

It is the most important feature of big data analysis. The volume here represents the amount of data extracted from a source. It determines the value and potential of the data to be classified among the big data.
But, describing it as huge does not specify a specific quantity. Rather, the measure here is by bits or byte. It is estimated that 90% of the data in the world today was generated during the last two years, by devices and by humans, both of which contributed to the increase in data.
Variety
It refers to the diversity of the extracted data. This variety helps researchers and analysts to choose the appropriate data for their field of research. It includes:
- Structured data retrieved from databases.
- Unstructured such as pictures, clips, audio recordings, videos, SMS and call records Map data (GPS).
Such a wide variety of data requires time and effort to prepare it in a suitable form for processing and analysis. The NoSQL approach is a suitable way to achieve good results.
Velocity
It covers the speed of production and extraction of data to fulfill the demand for it. Here, speed is crucial because it affects the decision that will be made based on this data.
“Batch processing” is the old approach to handle a small set of structured data where we analyze each set in a consecutive sequence. The huge increase in the volume and speed of data increase the need for a system that guarantees high speed in analyzing big data in real-time. This need has led to the innovation of technologies and solutions such as Apache, SAP HANA, Hadoop, and many others.
Sources

It comes from running a program, whether it is a governmental or non-governmental program, such as electronic medical records, hospital visits, insurance records, bank records, and food banks.

Commercial or transactional related sources, arising from transactions between entities. For example credit card transactions and online transactions including mobile devices.

For example, satellite imaging, road sensors, climate sensors, tracking device sources, such as tracking information from cell phones and the Global Positioning System (GPS).

For example, the number of Internet searches for a product, service, or other types of information, and the number of views of a page on the Internet.

Such as comments on social media.
Conclusion
In our time, we are witnessing a huge explosion in information. The analysis and processing of it mainly increase the understanding and assimilation of customer requirements. Thus, increasing efficiency and productivity and reducing losses for companies. With time and technological advances, we expect significant progress in addressing the challenges and constraints of using big data more broadly.
Feel free to leave a comment or to Contact Me for an open discussion!
